Everything You Need To Know About Website Accessibility
Web accessibility is defined as delivering equal access to your data and services regardless of the user’s disability status. By developing trust and enhancing the user experience, you will attract a larger audience and strengthen your brand image.
What is Website Accessibility?
The term “website accessibility” describes how easily people with disabilities can use a website. This can include people who are blind or have limited vision, who are deaf, or have hearing problem. People with mobility limitations, cognitive problems, and others.
It means creating your website with accessibility and functionality in mind for all users. Including those who might need assistive technologies like speech recognition software, screen readers, or specialized input devices.
Why Is Web Accessibility Important?
Web accessibility improves the accessibility and grasp of your website’s content for all users. This include people with limitations and disabilities
Four Principles of Accessibility
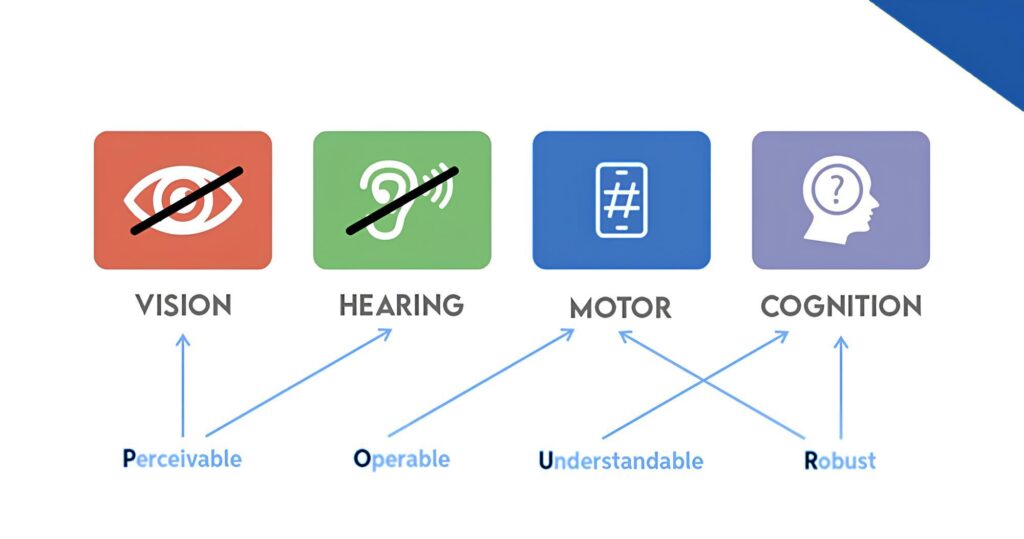
The principles of website accessibility serve as the foundation for any content created for the web and anybody who wants to utilize it. These principles are known as POUR, this abbreviation specifies functional accessibility:
Perceivable
Perceivability is the quality of having all information and UI components presented in a way that allows each sense to pick up on them and ensures that nothing is hidden or difficult to perceive. Most online users detect perceivability mostly through visuals; however, individuals who are unable to do so depend on sound and touch.
Read our blog: Everything You Need To Know About Wi-Fi 7
Operable
The website should be user-friendly for everyone. This idea ensures that all users can navigate and control the website in a variety of ways.
If a user does not have access to a mouse or does not have it, you can encourage them to use a keyboard to surf the website. To make sure your website is safe for users with disabilities, you should also remove any flashing or autoplaying features that may cause seizures.
Understandable
Both the content and the website’s operation should be simple to understand. In other words, the website must provide readable material in a well-organized framework with predictable navigation.
Robust
According to this principle, all web browsers and user agents, including those that support assistive technology, must be able to view the site’s content.
You can do this by staying up-to-date on the newest information and digital communication standards, such as HTML5 and CSS3.
How To Make An Accessible Website?
According to WCAG standards, the W3C Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) established and benchmarked the following principles that characterize accessible solutions:
Must Include Alt Text:
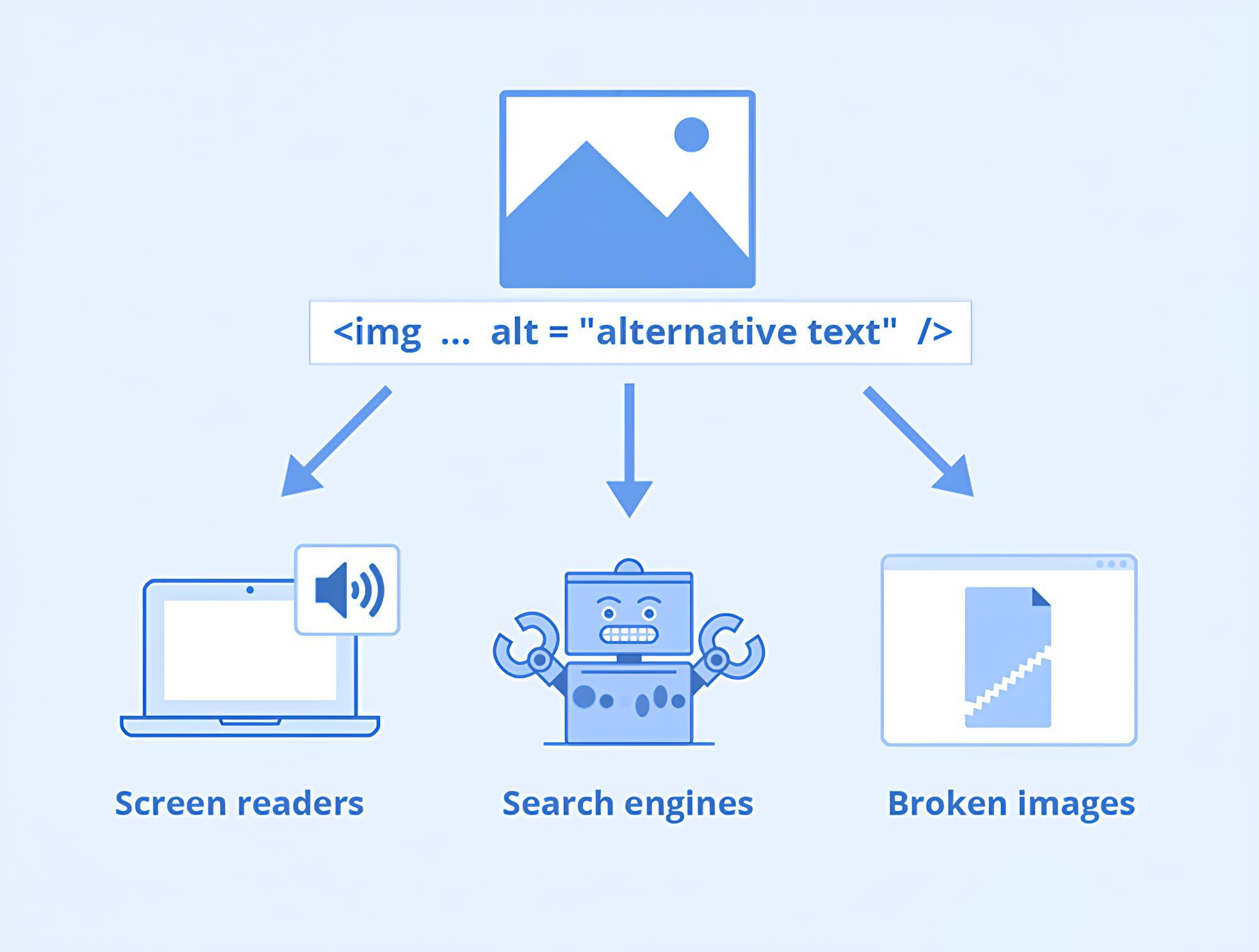
Images should have alternative text (alt text) in the markup/code. If alt text is not given for pictures, the image information is unavailable to blind people. The information is accessible to both the visually impaired and those who are unable to see when you give similar alt text. It would be accessible to search engines too, which can not process images.
Keyboard Navigation
Users with limited mobility must have an alternate way to access your website. Allowing users to navigate around and between web pages with a keyboard shortcut. Instead of a mouse, is an essential aspect of accessible websites.
In addition, a number of websites allow visitors to “skip to the content” and bypass the page’s navigation menu, which would take a lot of tabs to navigate. Another way to make your website accessible and keyboard-friendly is to use breadcrumbs. Breadcrumbs allow visitors to navigate back to a previous page.
Make accessible and readable content

To provide inclusivity for those with cognitive limits and learning difficulties. The text’s understanding level should be made feasible for a wide range of audiences. People who cannot see or hear the material or who might not be able to understand implicit linkages, sequences, or other indications on site components, including forms, may benefit from this.
Write parsable HTML:
The HTML file on a web page is frequently used by assistive technology to convert its information into another format. Because of this, the HTML code on your pages has to be well-written. Using start and end tags where necessary, avoiding duplication IDs across components, and avoiding duplicate attributes inside the same HTML tag.
Conclusion:
Making sure your website is accessible is the appropriate thing to do for the people who matter most to your company: your clients and guests. Your website should be examined while it is being developed or redesigned. This can guarantee that problems are found early and are quickly fixed. While there are several tools available to help with the evaluation procedure.
Read our blog: Everything You Need To Know About Email Marketing

